https://engineers.academy/level-5-higher-national-diploma-courses/In this video, we expand on the principles covered in our introduction to second order diff.. Second Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients: a2y ′′(t) +a1y′(t) +a0y(t) = f(t), where a2 6= 0 ,a1,a0 are constants, and f(t) is a given function (called the nonhomogeneous term). General solution structure: y(t) = y p(t) +y c(t) where y p(t) is a particular solution of the nonhomog equation, and y

nonhomogeneous second order differential equation lectrue 12 YouTube
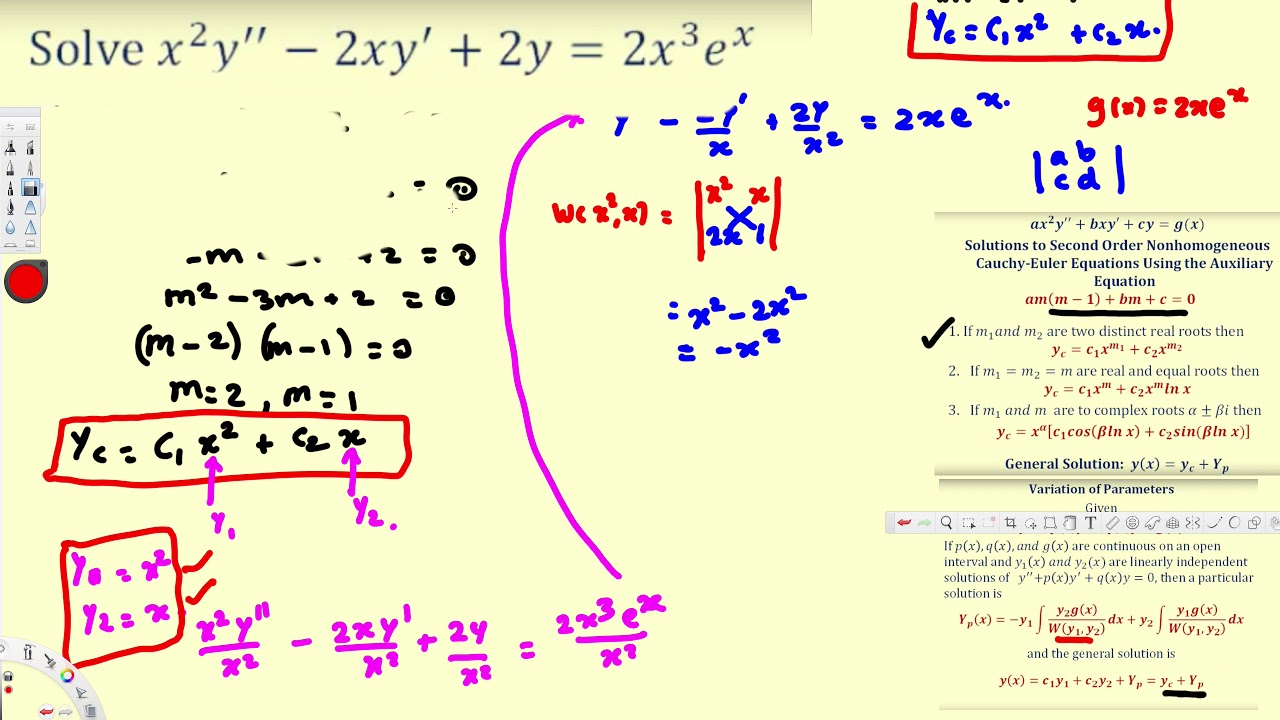
Second Order Nonhomogeneous Cauchy Euler Differential Equations YouTube

Non Homogeneous Second Order Linear Differential Equations Part 2 YouTube

Variation of parameters Solving Nonhomogeneous Second Order Differential Equations Part 5
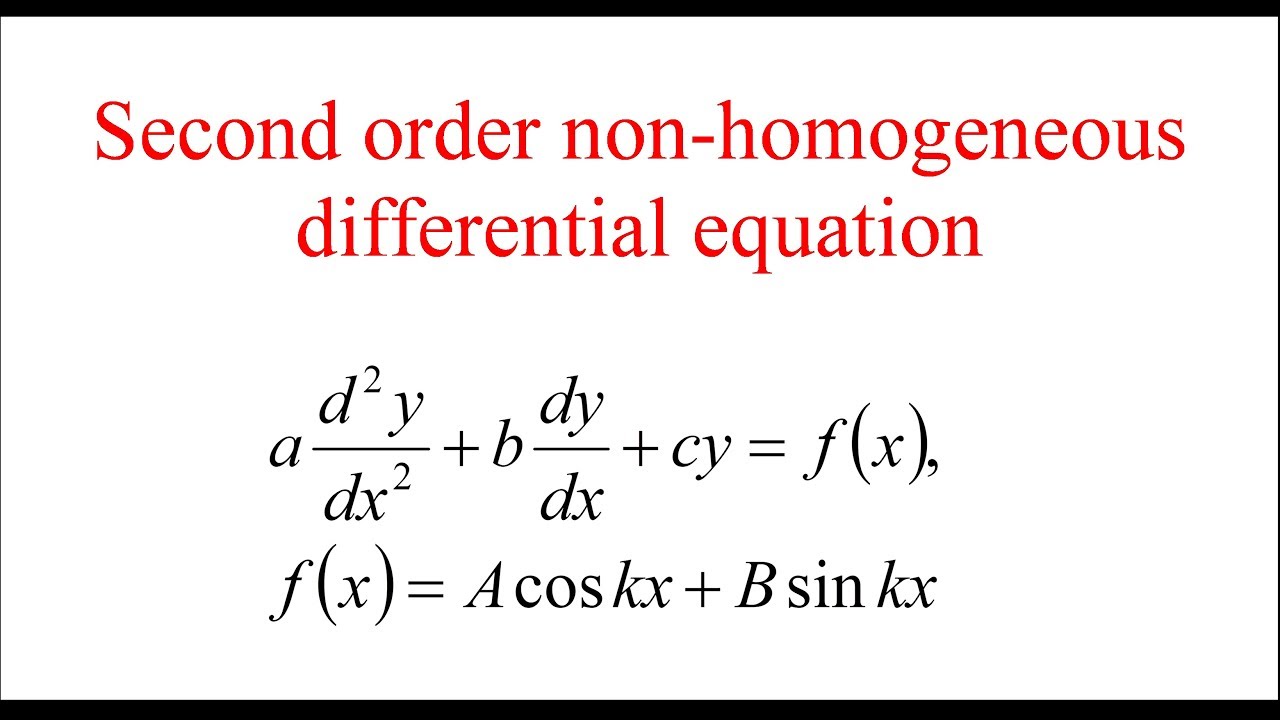
Second order nonhomogeneous differential equation YouTube

Solved A nonhomogeneous 2ndorder differential equation is
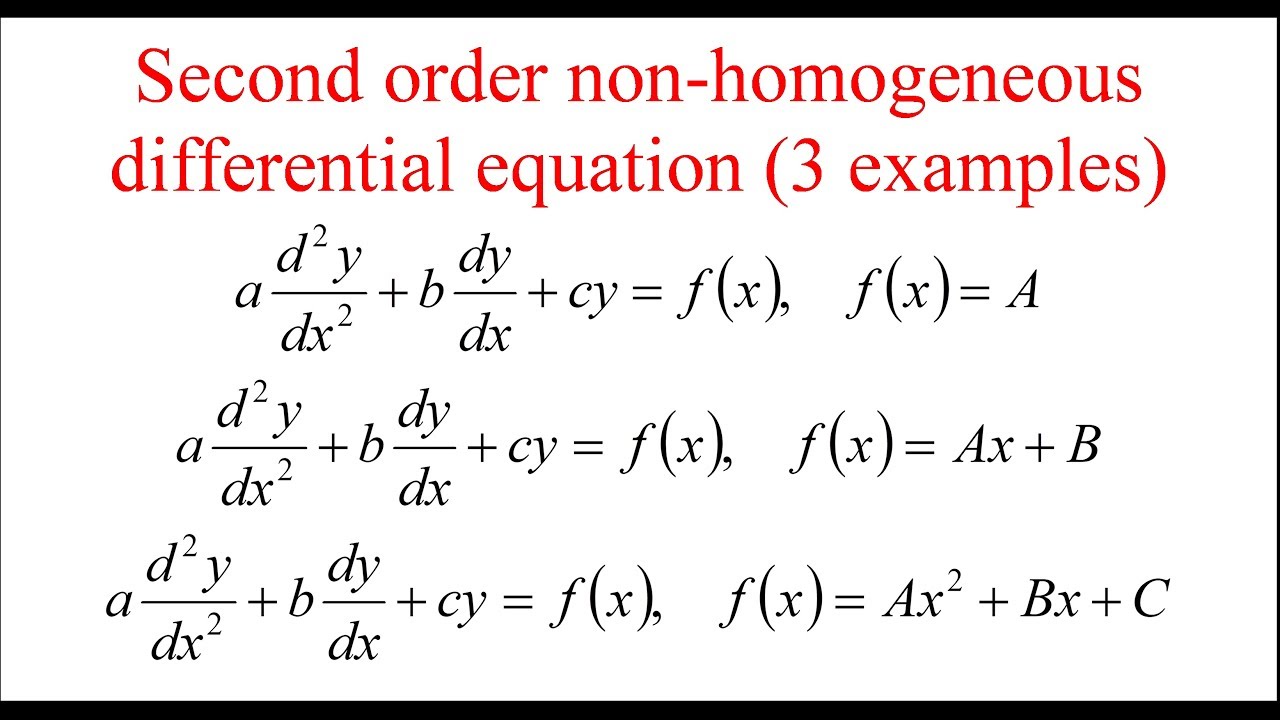
Second order non homogeneous differential equation YouTube

Solving NonHomogenous Second Order Differential Equations YouTube
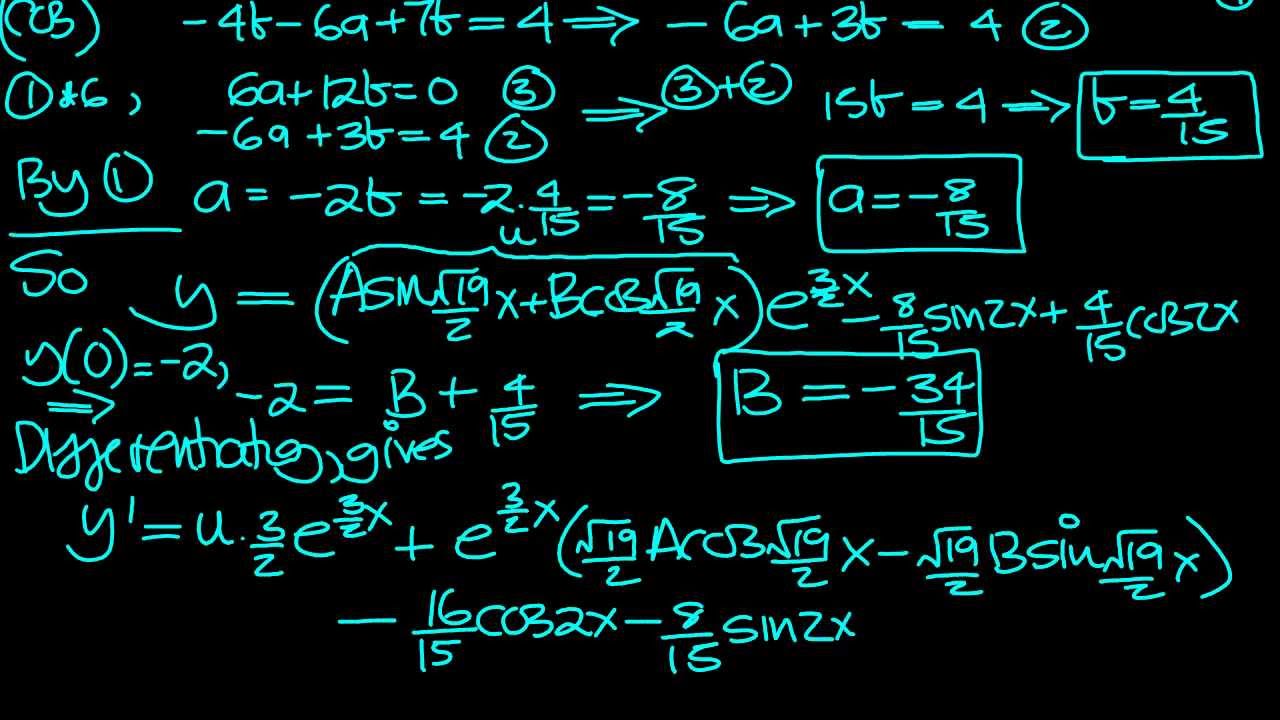
Second Order Non Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations with ics Q2 YouTube
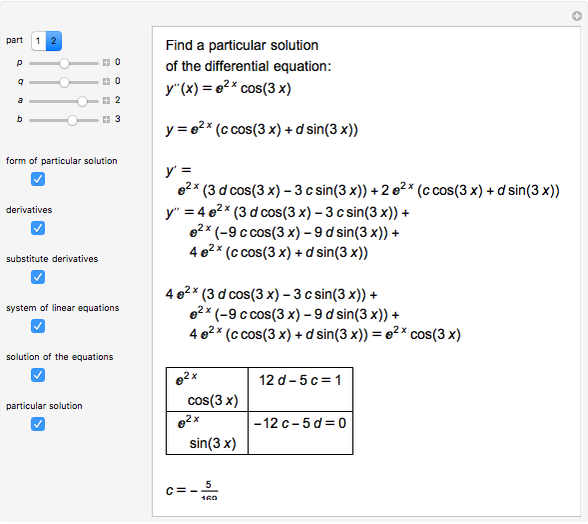
Particular Solution of a Nonhomogeneous Linear SecondOrder Differential Equation with Constant

Nonhomogeneous 2ndorder differential equations YouTube

Second Order Non Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations Q10 YouTube
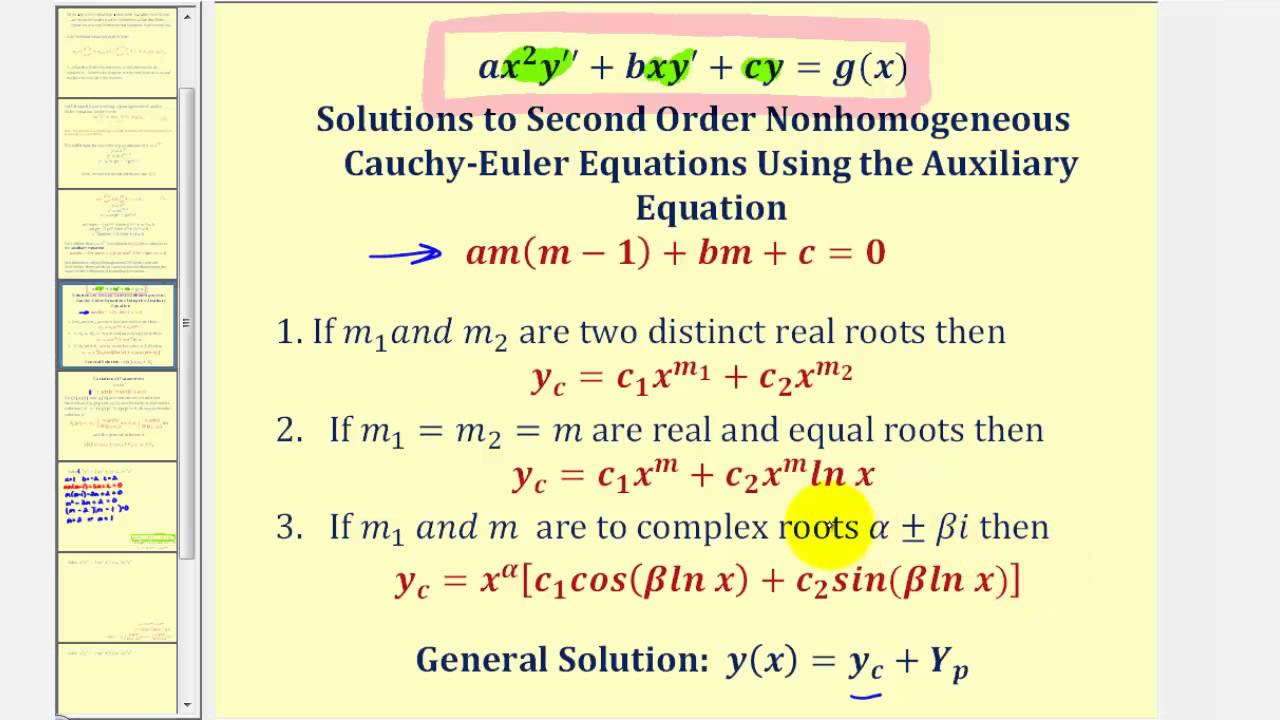
Second Order Nonhomogeneous CauchyEuler Differential Equations YouTube

Second order nonhomogeneous differential equation YouTube
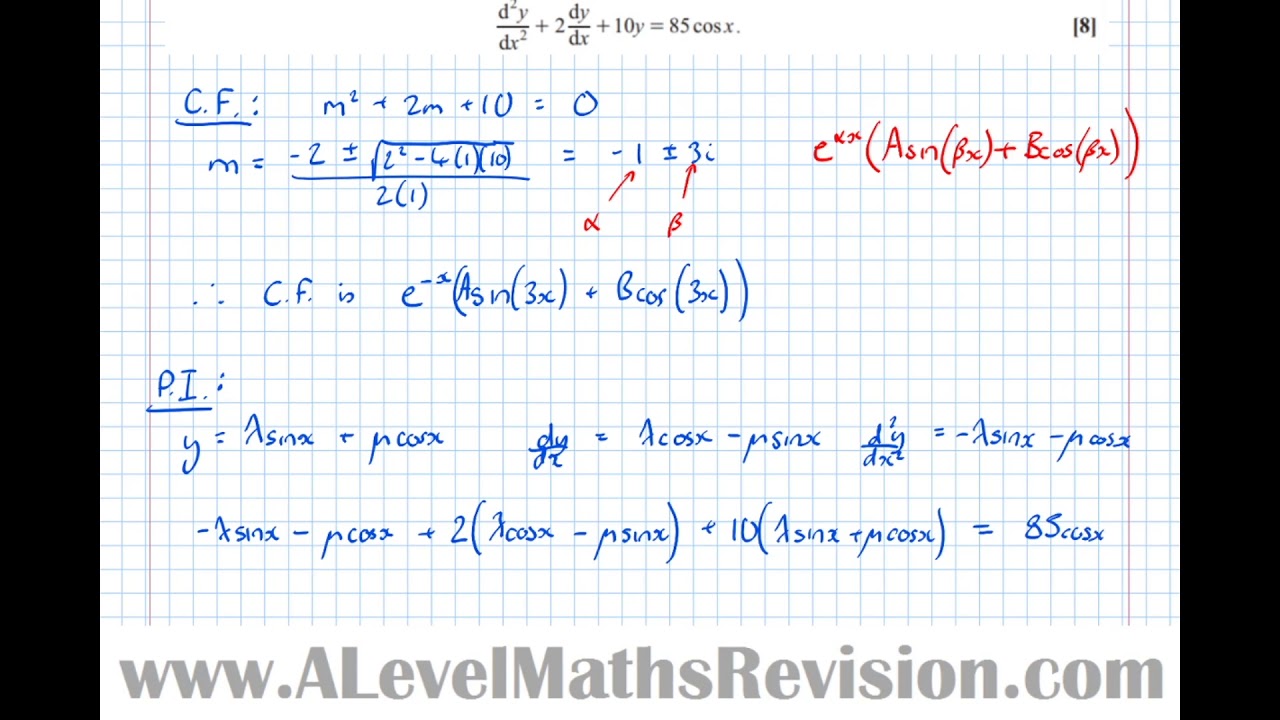
Nonhomogeneous Second Order Differential Equations Exam Question [Year 2 Further (Pure Core

SecondOrder NonHomogeneous Differential Equation Initial Value Problem (KristaKingMath) YouTube

Undetermined Coefficients method Solving Nonhomogeneous second Order Differential Equations

Solved 0.22 The nonhomogeneous second order differential

2nd Order Linear Differential Equations Particular Solutions ExamSolutions YouTube

(PDF) Second Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Differential Equations; Method of Undetermined
second order differential equation: y" p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. Find the particular solution y p of the non -homogeneous equation, using one of the methods below. 3. The general solution of the non-homogeneous equation is: y(x) C 1 y(x) C 2 y(x) y p where C 1 and C 2 are arbitrary constants. METHODS FOR FINDING THE PARTICULAR SOLUTION (y p) OF A NON.. Example 2. Find the general solution of the equation. Solution. We will use the method of undetermined coefficients. The right side of the given equation is a linear function Therefore, we will look for a particular solution in the form. Then the derivatives are. Substituting this in the differential equation gives: The last equation must be.